Concrete Table Inheritance
Represents an inheritance hierarchy of classes with one table per concrete class in the hierarchy.
- Overview
- How It Works
- When to Use It
- Advantages
- Disadvantages
Overview
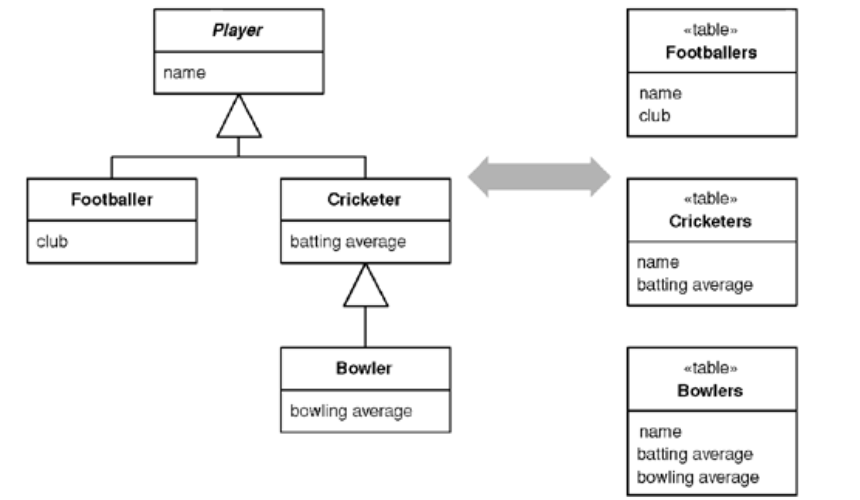
Take each object in memory and map it to a single database row. With Concrete Table Inheritance, there’s a table for each concrete class in the inheritance hierarchy.
Most people think of it as a leaf oriented since you usually have one table per leaf class in a hierarchy. Strictly, however, a concrete class that isn’t a leaf ususally gets a table as well.
How It Works
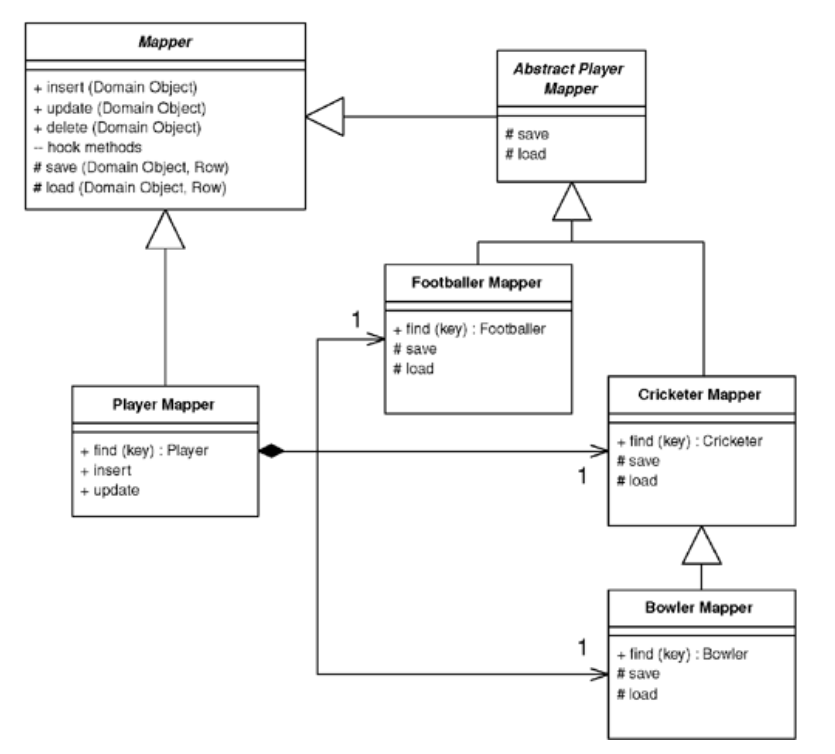
Concrete Table Inheritance uses one database table for each concrete class in the hierarchy. Each table contains columns for the concrete class and all it ancestors, so any fields in a superclass are duplicated across the tables of the subclasses.
The basic behavior uses Inheritance Mappers. It’s important to ensure that keys are unique not just to a table but to all the tables from a hierarchy.
A classic example of where you need this is if you have a collectio nof players and you’re using Identity Field with table-wide keys. If keys can be duplicated between the tables that map the concrete classes, you’ll get multiple rows for a particular key value.
When to Use It
Class Table Inheritance, Single Table Inheritance and Concrete Table Inheritance are the three alternatives to consider for inheritance mapping.
Advantages
-
Each table is self-contained and has no irrelevant fields. As a result it makes good sense when used by other applications that aren’t using the objects.
-
There are no joins to do when reading the data from the concrete mappers.
-
Each table is accessed only when that class is accessed, which can spread the access load.
Disadvantages
-
Primary keys can be difficult to handle.
-
You can’t enforce database relationships to abstract classes.
-
If the fields on the domain classes are pushed up or down the hierarchy, you have to alter the table definitions.
-
If a superclass field changes, you need to change each table that has this field (because the superclass fields are duplicated across the tables).
-
A find on the superclass forces you to check all the tables, which leads to multiple database accesses (or a weird join).