Apache HBase
- Overview
- Column Oriented Storage
- Use Cases
- CP Type System
Overview
Hbase is an open-source non-relational distributed database modeled after Google’s Bigtable and written in Java. It is developed as part of Apache Haddop project and runs on top of HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System) or Alluxio, providing Bigtable-like capabilities for Hadoop. That is, it provides a fault-tolerant way of storing large quantities of sparse data
Sparse data: small amounts of information caught within a large collection of empty or unimportant data. Sparse data contain many meaningless values (i.e. zero).
Hbase features compression, in-memory operation, and Bloom filters on a per-column basis as outlined in the original Bigtable paper.
Tables in HBase can serve as the input and output for MapReduce jobs run in Hadoop, and may be accessed through the JAVA API but also through REST, Avro, or Thrift gateway APIs.
HBase is a wide-column store, well-suited for fast read and write operations on large dataseets with high throughput and low I/O latency.
HBase is optimized for operations such as finding the 50 largest items in a group of 2 billion records, or finding the non-zero items representing less than 0.1% of a huge collection.
Column Oriented Storage
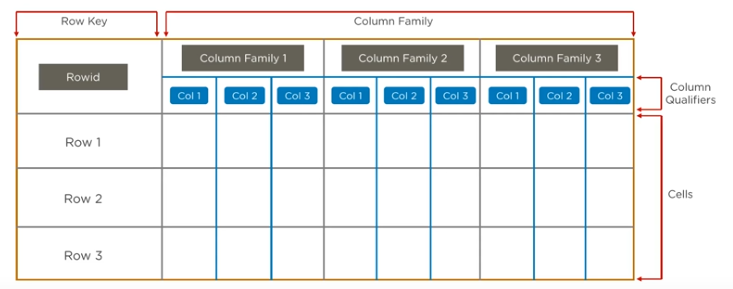
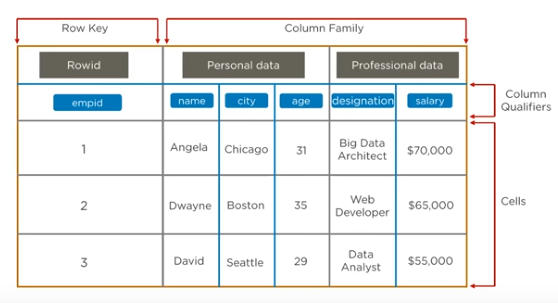
Use Cases
- Medical: storing genome sequences, disease history of people or an area.
- E-Commerce: storing logs about customer search history, perform analytics and target advertisement.
- Sports: match details and history for prediction.
CP Type System
In the parlance of Eric Brewer’s CAP *Theorem, HBase is a CP type system, meaning that it provides Consistency and Partition Tolerance guarantees, but not Availability guarantee.
Refer to CAP Theorem for more details.