Microservices Concerns
Configuration Management
Configuration needs to be externalized from the code and be retrievable via a simple service call.
-
Spring Config Service support a Git-repository based location for configuration.
-
Kubernetes ConfigMaps exposes the configuration stored in etcd via services. Kubernetes Secrets supports the service-based secure deployment and usage of sensitive configuration information.
Service Discovery
Maintain a list of servcice instances that are available for work within a microservice domain.
-
Spring Cloud Eureka allows clients to register to it, maintains a heartbeat with registered clients, and maps service names to hostnames for clients that lookup services by service name.
-
Kubernetes Service provide deployment-time registration of instances of services that are internally available within the cluster. Ingress is a mechanism whereby a service can be exposed to clients outside the cluster.
Load Balancing
The key to scaling a distributed system is being able to run more than one instance of a component. Load has to be then distributed across those instances via a load balancer.
-
Spring Cloud Ribbon provides the ability for service clients to load balance across instances of the service.
-
Kubernetes Service provides the ability for the service to be load-balanced across service instances.
API Gateways
The granularity of APIs provided by microservices is often different than what a service client needs. API Gateways implement facades and provide additional services like proxying, and protocol translation, and other management functions.
-
Spring Cloud Zuul provides the ability for service clients to load balance across instances of the service.
-
Kubernetes Service and Ingress resources, Istio, Ambassador are solutions that provide both north-south (traffic into and out of data center) as well as east-west (traffic across data centers or clouds or regions) API gateways functions. Zuul can also be implemented along with Kubernetes, providing configuration at individual service level.
Security Concerns
Many security concerns are pushed to the API gateway implementation. With distributed microservice applications, it makes sense to not reinvent the security wheel and allow for policy definition and implementation in components that are shared by all services.
- Spring Cloud Security addresses many security concerns through Spring Cloud Zuul.
- Kubernetes Ecosystem provides service meshes like Istio, which are capable of providing security through their API gateway mechanisms.
Centralized logging
it’s important to have a centralized log gathering and analysis infrastructure to manage a plethora of services.
- ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, LogStash, Kibana).
- EFK Stack (Elasticsearch, Fluentd, Kibana).
Centralized Metrics
A centralized area where the health and performance of the individual services and overall system can be monitored is essential.
- Spring: Spectator & Atlas.
- Kubernetes Ecosystem: Heapster, Prometheus, Grafana.
Distributed Tracing
There’s a need to reconstruct the complex paths that transactions take as they propagate across a distributed system.
- Spring Clous Sleuth.
- Kubernetes Ecosystem: Hawkular, Jaeger.
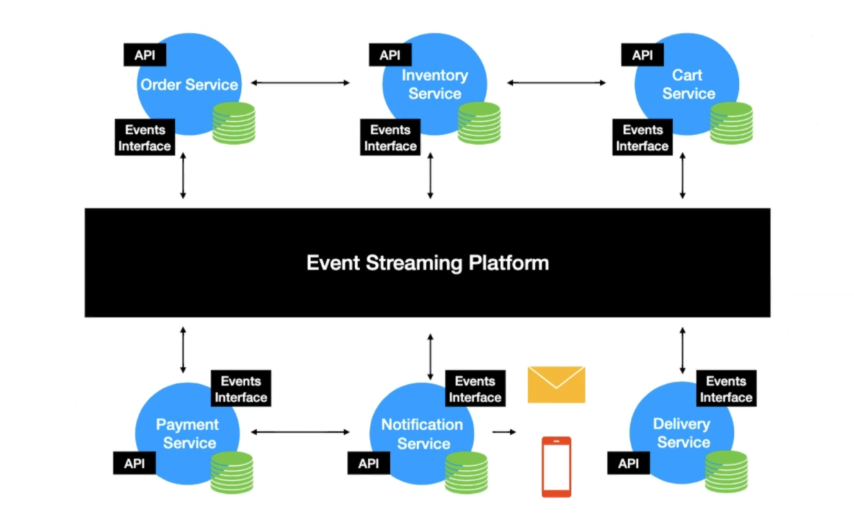
Event Streaming
Event streaming is the practice of capturing data in real-time from event sources (i.e, databases, sensors, mobile devices, cloud services etc) in the form of stream of events; storing these event streams durably for later retrieval; manipulating, processing, and reacting to the event streams in real-time as well as retrospectively; and routing the event streams to different destination technologies as needed.
Resilience and Fault Tolerance
Distributed systems must be capable of auto-routing around failures, and be capable of routing requests to the service instance that will provide an optimum response.
- Spring Hystrix, Turbine, & Ribbon.
- Kubernetes Ecosystem: Health check, service meshes (i.e, Istio).
Autoscaling and Self-healing
Distributed systems respond to higher load by scaling horizontally: the platform must detect and auto-respond to such conditions. Furthermore, the system needs to detect failures and attempt auto-restarts without operator input.
- Kubernetes Ecosystem: Health check, self-healing, and auto-scaling .
Packaging, Deployment and Scheduling
Large-scale systems require robust package management, and deployment systems to manage rolling or blue-green deployments, and rollbacks if necessary. A scheduler helps determine which particular execution node a new set of services can be deployed to based on current conditions.
- Spring Boot, Apache Maven, Spring Cloud System (does not have a true scheduler).
- Kubernetes Ecosystem: Docker, Rkt, Kubernetes Scheduler & Deployment, Helm.
Job Management
How to handle scheduled computations disconnected from any individual user requests.
- Spring Batch.
- Kubernetes: Jobs and Scheduled Jobs.
Singleton Application
Limit a specific service to run as the only instance of that service within the entire system.
- Spring Cloud Cluster.
- Kubernetes Pods