Stable Abstractions Rule
- Don’t refer to volatile concrete classes, refer to abstract interfaces instead.
- Don’t derive from volatile concrete classes.
- Don’t override concrete functions (you inherit its dependencies).
- Never mention the name of anything concrete and volatile.
Changes to concrete implementation do not always, or even usually, require changes to the interfaces they implement. Therefore interfaces are less volatile than implementations.
Indeed, good software designers and architects work hard to reduce the volatility of interfaces, and find ways to add functionality to implementations without making changes to the interfaces.
Factories
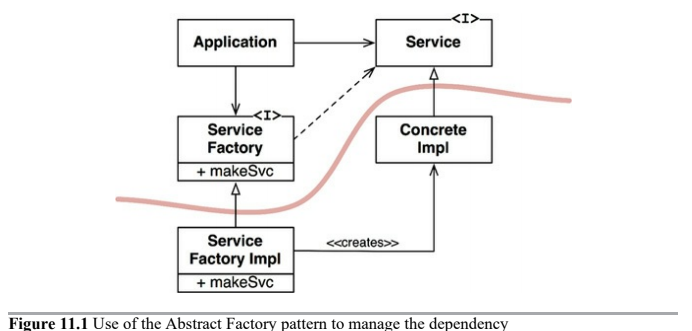
To comply with these rules, the creation of volatile concrete objects require special handling. This caution is warranted because, in virtually all languages, the creation of an object requires a source code dependency on the concrete definition of that object.
In most object-oriented languages, such as Java, we would use an Abstract Factory to manage this undesirable dependency.
The Application uses the ConcreteImpl through the Service interface. However, the Application must somehow create instances of the ConcreteImpl. To achieve this without creating a source code dependency on the ConcreteImpl, the Application calls the makeSvc method of the ServiceFactory interface. This method is implemented by the ServiceFactoryImpl class, which derives from ServiceFactory. That implementation instantiates the ConcreteImpl and returns it as a Service.